General Journal Entries
The Online System contains a General or Plain Language Journal Entries Report
on the Accounting / Interface Menu. The General Journal Entries is
the simplest and easiest way to interface with external accounting programs such
as QuickBooks®.
To run the report, select a starting date,
ending date, and a location (for multi-location operators), and then click the
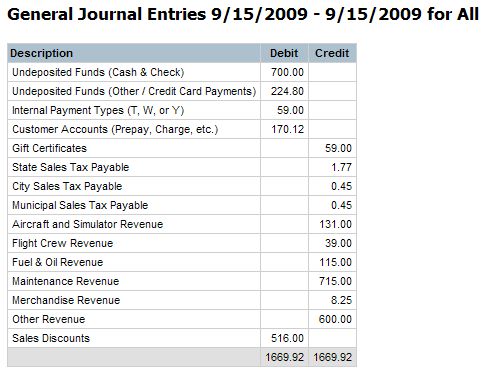
Go button. The Journal Entry Report is a summary and has 16 possible items:
- Un-deposited Funds (Cash & Check) - Total Cash and Check
payments you received for the given date range. This account usually has a
debit balance.
- Un-deposited Funds (Other / Credit Card Payments) - Total other
payments you received for the given date range. Other payments are usually
credit card payments. This is a separate line on the report because
sometimes further accounting is required, such as expensing credit card
fees. This account usually has a debit balance.
- Internal Payment Types (T, W, or Y) - Internal payment types from
the Payment and Card Type parameters. Types T, W, and Y do not appear in
Online System's cash drawer. For example, many Subscribers use these payment
types to "write off" a transaction. If this is the case at your
operation, you could debit a "bad debt expense" or similar account
in your external accounting software. This account usually has a debit
balance.
- Customer Accounts (Prepay, Charge, etc.) - Sum of customer
accounts. Customer accounts can include Prepay, Charge, Special, and Urgent.
This line could have a debit or credit balance depending on the types of
accounts and how they change position. For example, a prepay balance is a
liability and increased with a credit. When a customer uses some of their
prepaid funds, the liability is reduced with a debit. Here is how a
prepayment account journal entry breaks down:
Cash (Asset) = Debit
Prepaid Account (Liability or Negative A/R) = Credit
Explanation: Customer Funds Account
Prepaid Account (Liability or Negative A/R Reduced) = Debit
Revenue = Credit
Explanation: Customer uses Funds
The reverse is true for charge accounts. Note, in most external accounting programs,
Customer Accounts is setup as an Accounts Receivable (A/R) Account.
External accounting programs seem to handle negative Accounts Receivable
better than they handle a positive Accounts Payable.
- Gift Certificates - Sum of gift certificate sales and redemptions
for the given date range. This line could have a debit or credit balance.
When a gift certificate is sold, it is a liability, and when it is redeemed, it
is revenue. Here is how it breaks down:
Cash (Asset) = Debit
Gift Certificate (Liability) = Credit
Explanation: Gift Certificate Sold
Gift Certificate (Liability Removed) = Debit
Revenue = Credit
Explanation: Gift Certificate Redeemed
- State Sales Tax Payable - Sum of sales taxes charged and collected.
Usually a credit balance.
- City Sales Tax Payable - Sum of city sales taxes charged and
collected (if local taxes enabled in your system). Usually a credit balance.
- Municipal Sales Tax Payable - Sum of municipal sales taxes charged
and collected (if local taxes enabled in your system). Usually a credit
balance.
- Aircraft and Simulator Revenue - Sum of revenues associated with
aircraft and simulator operations. Usually a credit balance.
- Flight Crew Revenue - Sum of revenues associated with staff.
Usually charter pilots and flight instructors. Usually a credit balance.
- Fuel & Oil Revenue - Sum of revenues associated with fuel and
oil. Usually a credit balance.
- Maintenance Revenue - Sum of revenues associated maintenance, such
as maintenance labor and parts. Usually a credit balance.
- Merchandise Revenue - Sum of revenues for merchandise sold. Usually
a credit balance.
- Other Revenue - Sum of revenues for any items sold, not
associated with a revenue account above, such as "general
revenue". Usually a credit balance.
- Sales Discounts - Sales discounts or credits from the receipts.
These can include special offers, rebates, and general credits. Usually a
debit balance. Sales discounts is a contra-revenue account.
- Cash Expenditures - Appears if you allow cash expenditures from
your cash drawer and if you have a cash expenditure. Many times this is
handled as "petty cash". Usually a debit
balance.
The Journal Entry Report also has a total at the bottom. If the sum of the
debits does not match the sum of the credits, a red "Out
of Balance" message will appear. If the report is out of
balance, it is likely someone managed to do something weird while creating a
receipt.
General Journal Entries Report
09/01/09 P

